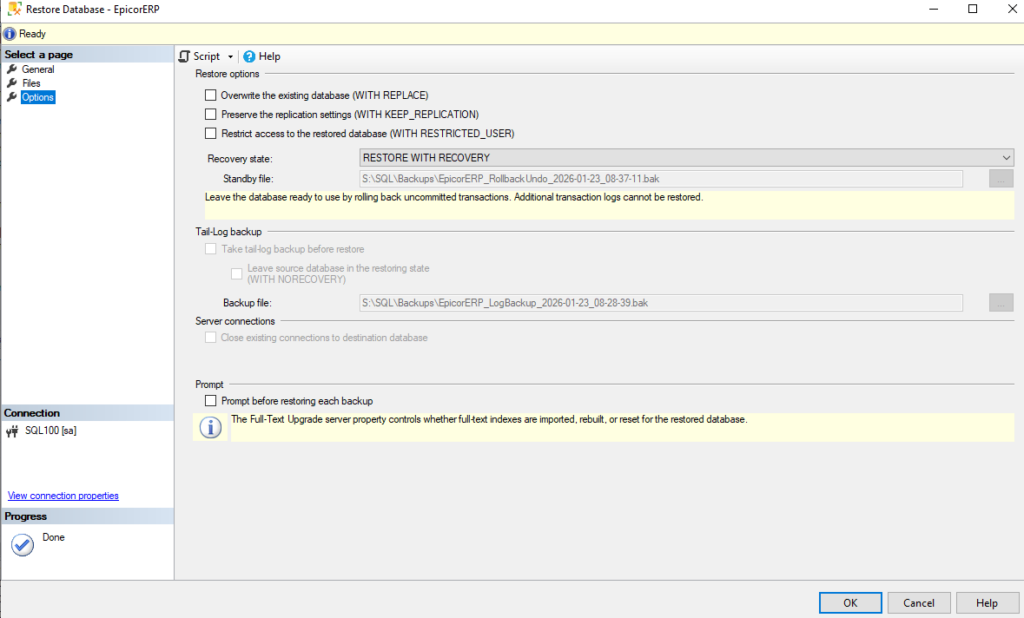
Restore EpicorERP with the Production full database backups
To restore a SQL Server database from a .bak file to a new database, you can use either SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Transact-SQL (T-SQL) commands. The key is to specify a new database name and relocate the physical data (.mdf) and log (.ldf) files to avoid conflicts.
Using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
This is the recommended method for most users due to its graphical interface.
- Connect to the appropriate SQL Server instance in Object Explorer.
- Right-click the Databases node and select Restore Database.
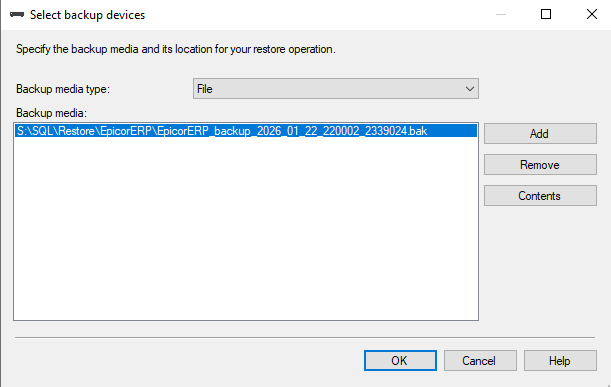
- In the Source section, select Device and then click the browse (…) button to locate your
.bakfile.- In the Select backup devices dialog, click Add, navigate to the
.bakfile’s location, select it, and click OK. - Click OK again to return to the main Restore Database window.
- In the Select backup devices dialog, click Add, navigate to the
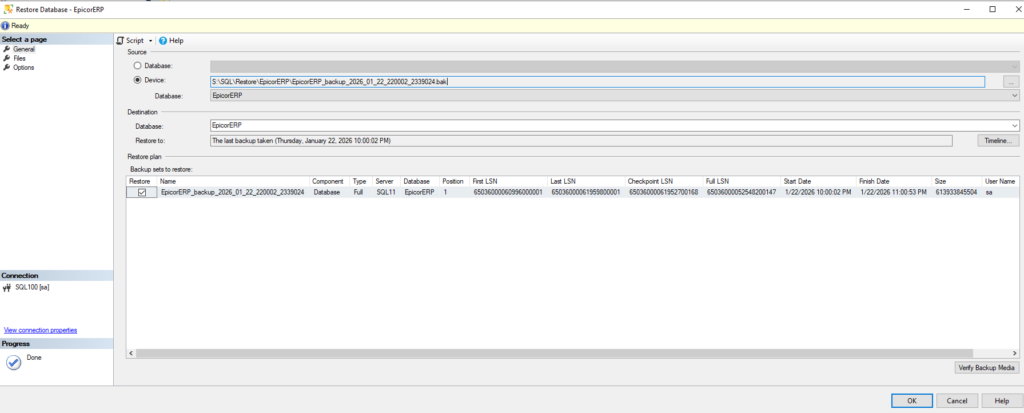
- In the Destination section, the Database box will be automatically populated with the original database name. Enter a new name for your new database here.
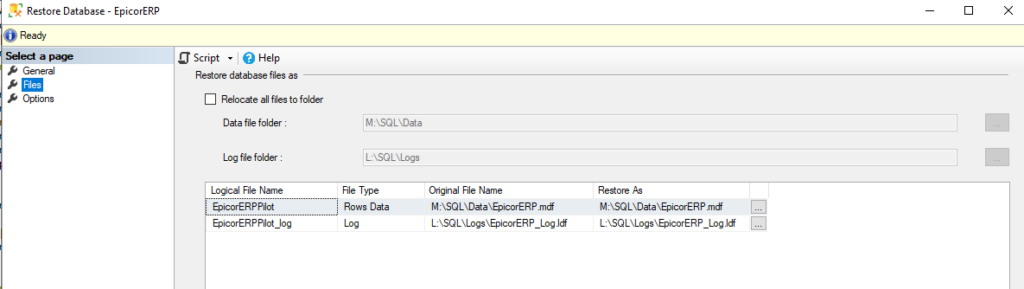
- In the “Select a page” pane, click on Files.
- Under the Restore the database files as grid, ensure the Restore As column has unique file paths and names for the new
.mdfand.ldffiles. This step is crucial to prevent conflicts with the original database’s files. - In the “Select a page” pane, click on Options. Under Restore options, you can optionally check Close existing connections to ensure the restore process can obtain exclusive access.
- Click OK to begin the restore process. A confirmation message will appear upon successful completion.
Using Transact-SQL (T-SQL)
For a command-line approach, you can use the RESTORE DATABASE statement with the MOVE option.
First, you need to find the logical names of the data and log files within the backup file by running RESTORE FILELISTONLY.
sql
RESTORE FILELISTONLY FROM DISK = N'C:\Path\To\YourBackupFile.bak';
This command returns the logical file names (e.g., OriginalDB_Data, OriginalDB_Log) which you will use in the next step.
Then, execute the RESTORE DATABASE command, replacing the placeholders with your specific names and paths:
sql
RESTORE DATABASE [YourNewDatabaseName]
FROM DISK = N'C:\Path\To\YourBackupFile.bak'
WITH
MOVE N'OriginalLogicalDataFileName' TO N'C:\New\Path\For\YourNewDatabaseName.mdf',
MOVE N'OriginalLogicalLogFileName' TO N'C:\New\Path\For\YourNewDatabaseName_log.ldf',
RECOVERY;
[YourNewDatabaseName]is the name you want for the new database.C:\Path\To\YourBackupFile.bakis the path to your backup file.OriginalLogicalDataFileNameandOriginalLogicalLogFileNameare the logical names obtained from theRESTORE FILELISTONLYoutput.C:\New\Path\For\...are the new physical file locations on the server’s file system.WITH RECOVERYensures the database is operational immediately after the restore.
Select a page:
Files:
Options: